Executive Summary
Bitcoin is far more than a buzzword in the financial headlines. It represents an evolving digital monetary system, a borderless network of value exchange that bypasses traditional intermediaries. While skeptics label it speculative or volatile, supporters argue that Bitcoin, with its finite supply and decentralized design, challenges long-standing economic norms and central bank control. Today, in a world grappling with inflation, political tensions, and rapidly changing technologies, Bitcoin forces us to re-examine what money can be—and what it could become.
Introduction: Rethinking Money in a Digital Age
Ask yourself, why do we trust national currencies or rely on established banks? The current system, while serviceable, often depends on the “good behavior” of intermediaries—governments and financial institutions that print money, set rules, and rescue “too-big-to-fail” banks. The 2008 financial crisis revealed structural weaknesses in this trust-based architecture, inspiring Bitcoin’s creation in 2009 as an alternative financial network.
Bitcoin is internet-native money—no government issues it, and no single entity controls it. It’s a financial system running in blockchain, governed by code rather than committees. This shift has sparked curiosity, debate, and, for many, investment.
The Problems Bitcoin Aims to Solve
1. Trust-Based Financial Systems: Traditional finance thrives on trust—trust that banks safeguard savings and trust that governments won’t recklessly erode a currency’s value. Yet, history is littered with failures. Banks sometimes over-lend with minimal reserves and governments print money to solve problems, eroding purchasing power. For example, the British pound has lost about 70% of its purchasing power in 40 years. Meanwhile, in places like Argentina or Zimbabwe, hyperinflation decimates savings and wages, making stable alternatives like Bitcoin more than a fad—they become lifelines.
2. Currency Debasement and Inflation: In developed economies, inflation may seem modest. But even in the U.S., the dollar lost 25% of its purchasing power since 2020. In more fragile economies, the story is bleaker. Zimbabwe’s national currency collapsed under a 500 billion percent hyperinflation, forcing citizens to explore alternatives. Bitcoin’s fixed supply—capped at 21 million coins—appeals to those weary of money printing and monetary policy missteps.
3. Political Risk and Seized Assets: The modern geopolitical climate underscores the vulnerability of state-controlled assets. When authorities can freeze foreign reserves or seize citizen funds, wealth is at risk. Bitcoin’s neutral network—accessible to anyone, anywhere—offers a hedge against such political interference.
Bitcoin’s Core Principles and Mechanics
Bitcoin’s architecture rests on four key assurances:
Global Accessibility: Anyone with an internet connection can send or receive Bitcoin. No permission required.
Immutable Ownership: By controlling your private keys—think of these as secret passwords—you hold your wealth without reliance on a centralized authority.
Predictable Monetary Policy: Bitcoin’s issuance rate halves every four years, making its supply growth increasingly scarce and transparent.
Verifiability: Bitcoin’s public ledger allows anyone to audit the system. This radical transparency stands in contrast to the opaque workings of traditional finance.
Real-World Insights and Comparisons
Argentina’s Inflation Woes: Argentines have seen their currency lose value for decades. Bitcoin, while volatile, offers a store of value that isn’t tied to local monetary policy.
Zimbabwe’s Currency Turmoil: After several attempts to stabilize its currency, Zimbabwe turned to gold-backed notes. Meanwhile, Bitcoin quietly rose over 130% against a collapsing local currency in a single year.
El Salvador’s Experiment: By embracing Bitcoin as legal tender, El Salvador is testing whether a decentralized network can complement or replace traditional monetary frameworks.
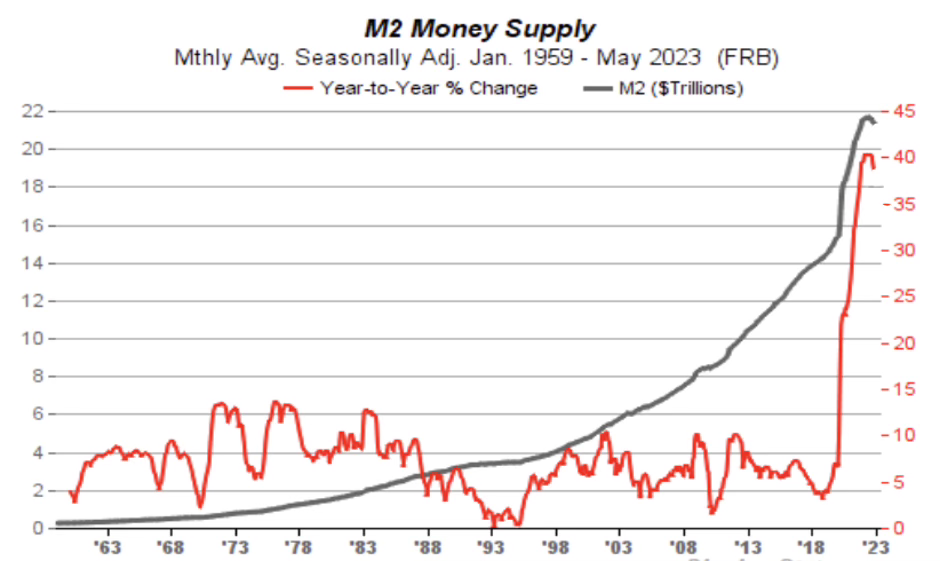
The U.S. Money Supply Surge: Since 2020, the U.S. has printed 80% of all Dollars in circulation, soaring from $4T to $19T—a 375% jump in just 3 years. No wonder inflation hit a 40-year high.
Visualizing the change in money supply
Source: The Kobeissi Letter
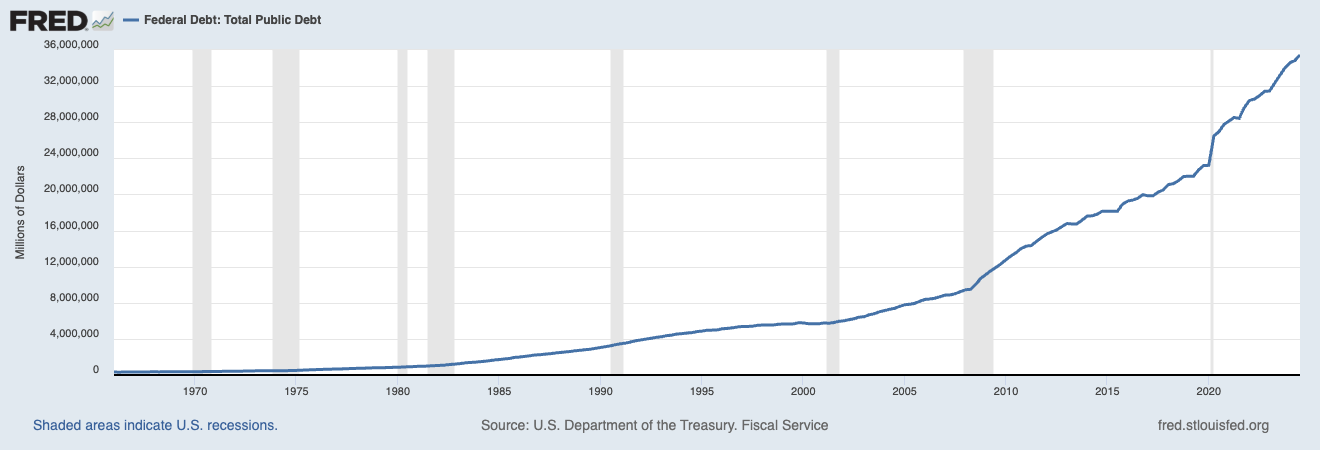
The U.S. holds 34.5% of global debt, with over $36 trillion and rising fast. Historically, debt spikes during wars—but this surge is happening in peacetime, raising serious concerns.
Opportunities and Advantages
Global Market Integration: Bitcoin’s borderless nature means it can facilitate trade and investment across countries with fewer barriers.
Diversification and “Digital Gold” Narrative: Some institutional investors view Bitcoin as a hedge against currency debasement, comparing it to gold. Its finite supply and secure infrastructure support this analogy.
Innovation in Payments and Finance: Companies like Square, PayPal, and Mastercard now integrate crypto services, hinting at more efficient, low-cost cross-border payments and new financial products.
Institutional adoption of Bitcoin is on the rise. Historically, institutions move in herds—once the early adopters take the leap, others quickly follow, transforming risk into 'normal' in their eyes. Momentum is building.
Empowering Individuals: In emerging markets, where traditional banking may be limited, Bitcoin provides direct access to global economic networks.
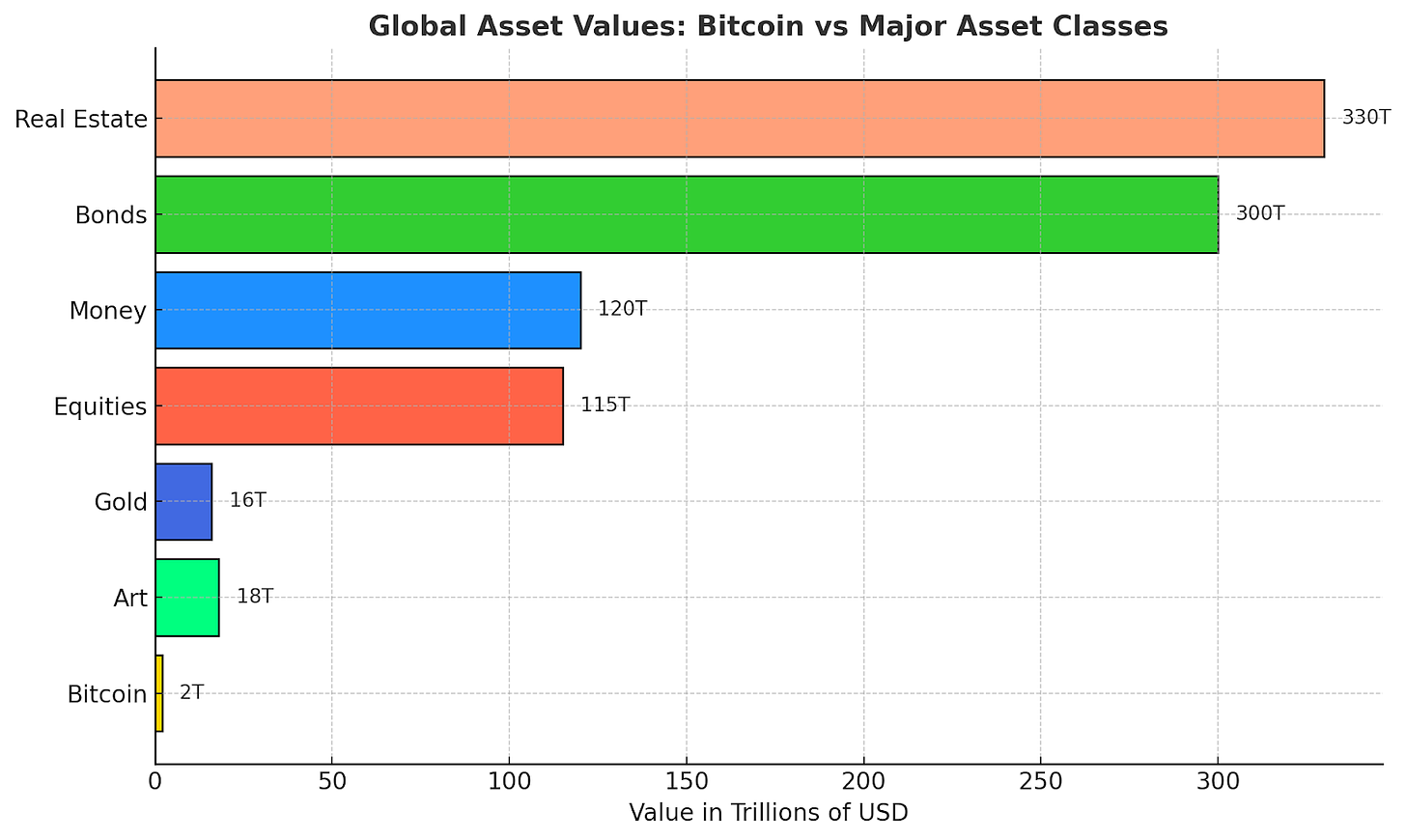
Bitcoin only makes just 0.2% of the global asset value. Bitcoin currently accounts for just 0.2% of global asset value, leaving massive room for growth as adoption accelerates. The future is still wide open
Challenges and Risks
Volatility and Speculation: Bitcoin’s price swings can be stomach-churning, sometimes rising or falling double-digit percentages in days. Such volatility attracts speculators and repels risk-averse investors.
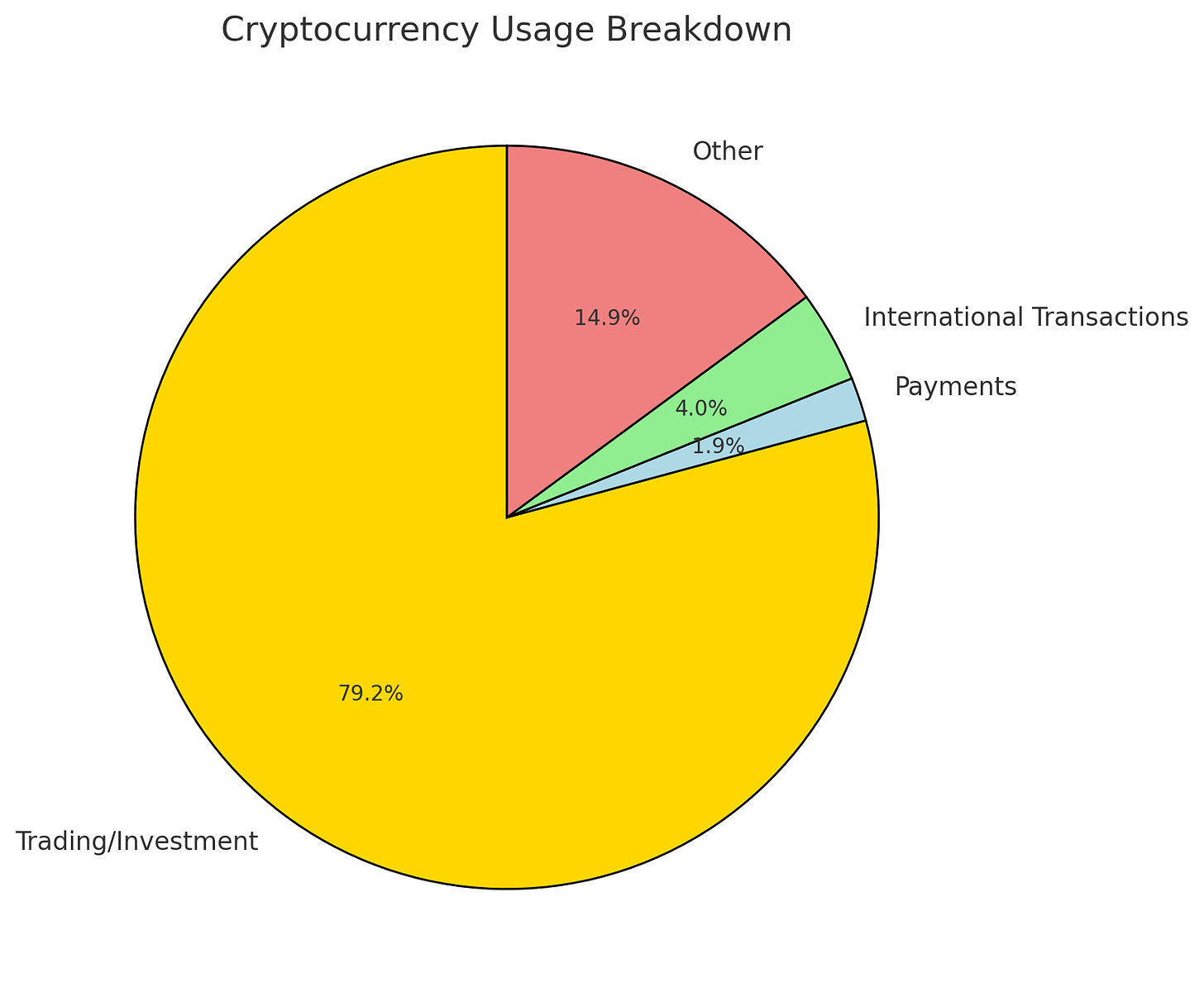
Most cryptocurrency owners—79.2%—use it for trading or holding as an investment, according to a study by the National Library of Medicine. On the other hand, just 1.9% use crypto for payments, and 4% for international transactions.This shows that while crypto thrives as an investment tool, its role in everyday transactions is still small. (Source: Kraken)
Regulatory Uncertainty: Governments may see Bitcoin as a threat. If it grows too influential, they could impose strict regulations or bans, curbing adoption. China’s crackdown on crypto activities highlights this possibility.
Security and Cyber Threats: While Bitcoin’s core network hasn’t been hacked, exchanges and wallets have suffered breaches. Holding digital assets securely remains a technical and psychological barrier. In addition, Quantum computing poses a potential long-term threat to cryptocurrency, but the risk is not immediate.
Environmental and Energy Concerns: Bitcoin’s mining process consumes substantial energy. Critics argue it’s unsustainable. New developments, alternative consensus mechanisms, and green energy solutions may address this, but concerns persist.
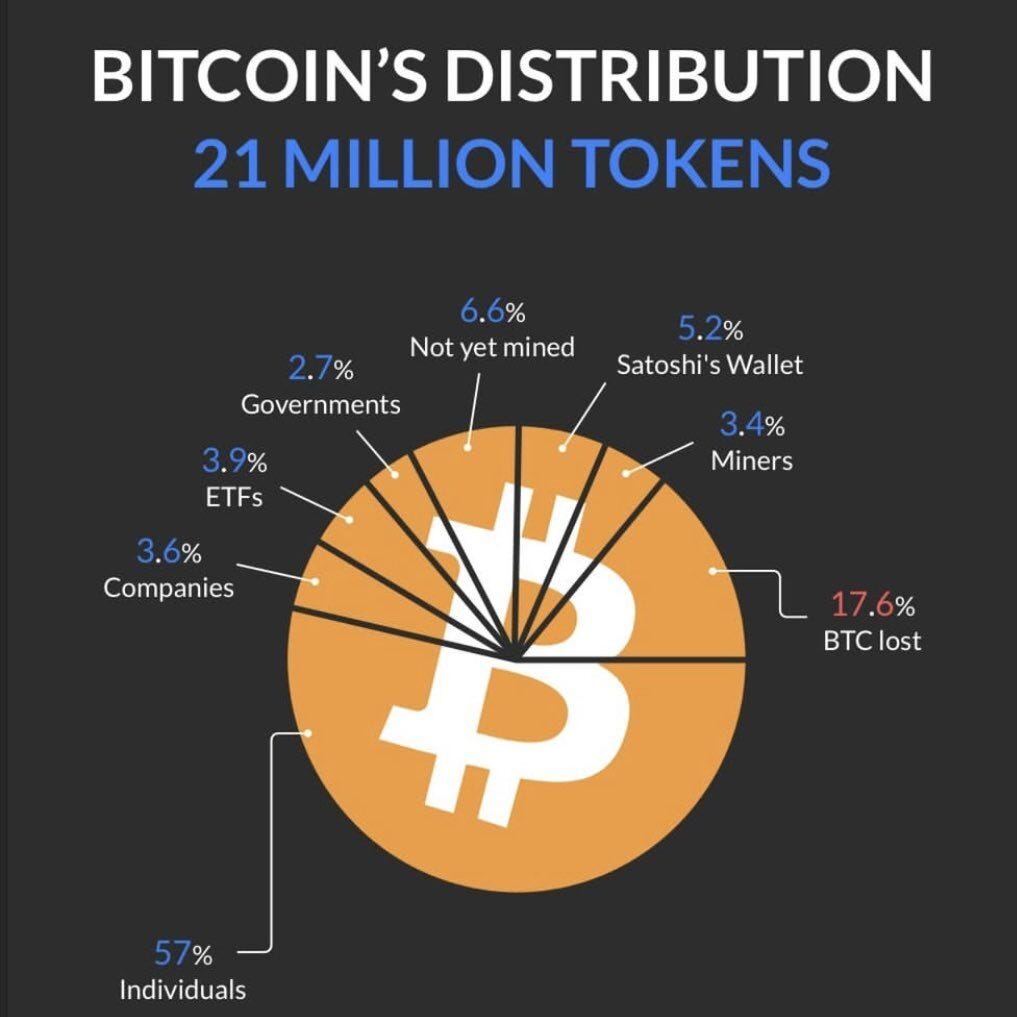
17% of Bitcoins Lost Forever? About 17% of all Bitcoins are lost—trapped in wallets without accessible keys. Early users often misplaced these “passwords,” saved them on discarded hard drives, or simply forgot where they wrote them down. Because Bitcoin has no recovery system, coins without private keys are locked forever. People have tried data recovery and even searching landfills, but success is rare. These lost coins remain on the blockchain as a permanent reminder that in a decentralized world, there’s no safety net if you lose your keys. It's a reminder to make sure you choose wisely who you deposit your bitcoin with.
Source: Cory Bates
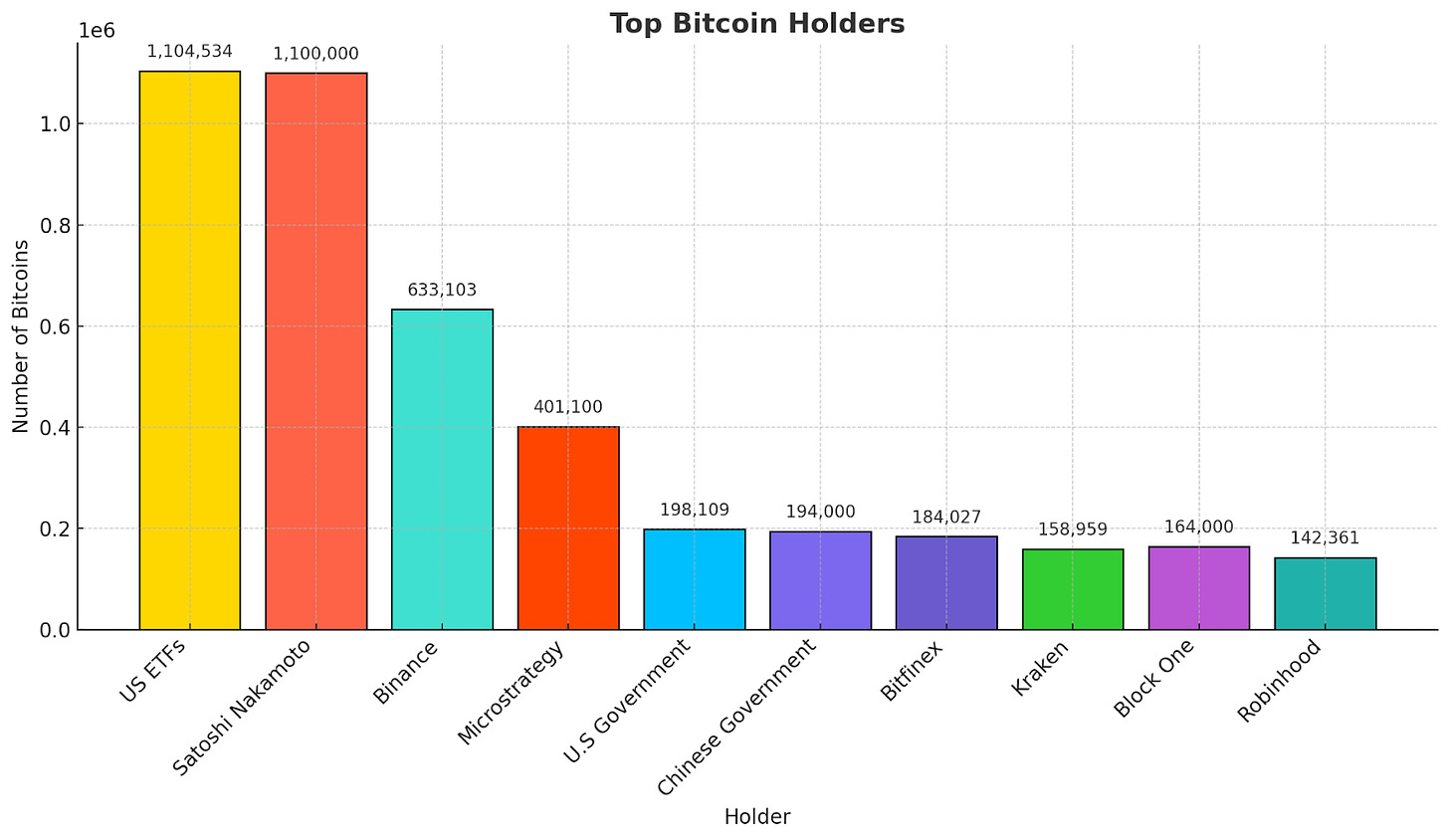
Concentration - Bitcoin ownership is dominated by a handful of major institutions and entities, highlighting its concentrated distribution among the biggest players in the crypto world.
Over 560 million people worldwide now own cryptocurrency: Adoption is growing, but for now, cryptocurrency is still mostly about speculation rather than everyday transactions.
Demographics:
🚹 61% Male | 🚺 39% Female
💰 Average Annual Income: $25,000
🎓 71% Hold a Bachelor’s Degree or Higher
🌟 Young & Growing: 72% are under age 34
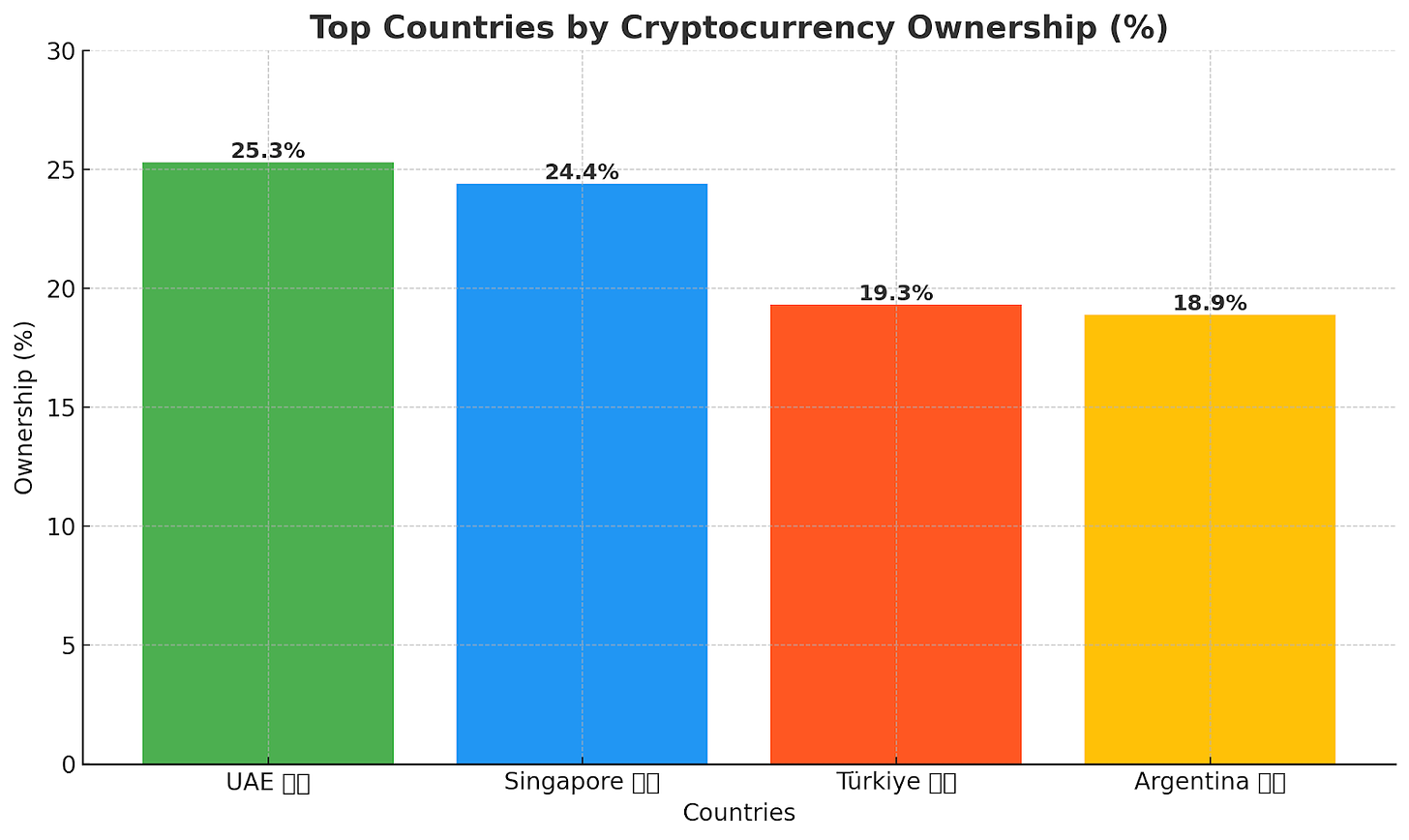
Top Countries by Ownership:
A Historical Perspective
Scrip and Speculation - In the 19th century, company-issued currencies (scrip) thrived in isolated economies. Their value hinged on a company’s stability. Once confidence waned, scrip became worthless. Similarly, Bitcoin relies on collective belief. Without confidence, its price could plummet. This historical lens reminds us that no monetary system is permanent. Caution and due diligence remain essential.
Institutional Views and Debates
Ray Dalio’s Balanced Skepticism: Prominent investor Ray Dalio acknowledges Bitcoin’s invention as remarkable, while warning of potential government clampdowns and competition from newer digital assets.
Larry Fink’s Perspective: BlackRock’s CEO suggests Bitcoin could rival major asset classes. But what if his optimism is misplaced? Without solid fundamentals, hype alone can’t sustain growth.
NFTs, Tokenization, and the Broader Crypto Landscape: Bitcoin is just the beginning. Blockchain technology powers Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs), decentralized finance (DeFi), and tokenized assets. These innovations hint at a future where wealth, art, property, and even identity exist on blockchains. While these are early days, the pace of change is rapid, and investors must stay alert to new opportunities and risks.
Forward-Looking Insights
Regulatory Clarity Will Shape Adoption: Clearer rules could unlock a wave of institutional investment. Bitcoin ETFs and custodial services might make it easier for pension funds, endowments, and large corporations to buy in.
Energy Solutions and ESG Considerations: Expect miners to seek cleaner energy sources to address environmental concerns. This could change the narrative around Bitcoin’s sustainability.
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs): Governments are exploring their own digital currencies, which could coexist or compete with Bitcoin. This might influence regulatory approaches and shape Bitcoin’s role in future financial systems.
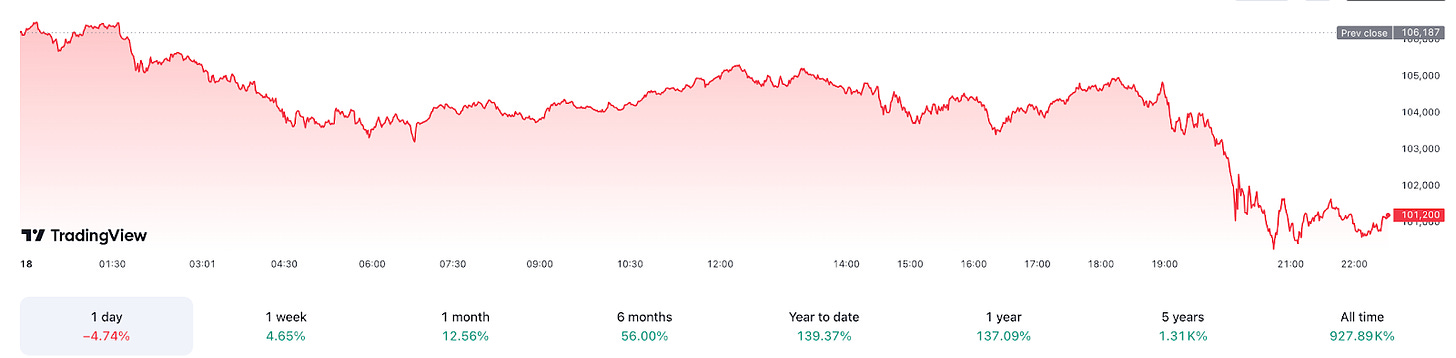
Performance
Bitcoin's price has skyrocketed over 930,700% since its inception and is up an impressive 139.57% just this year!
Actionable Takeaways for Investors and Stakeholders:
Assess Your Risk Tolerance: Bitcoin can be volatile. Only invest what you can afford to lose.
Focus on Education: Understand the underlying technology, the macroeconomic forces at play, and your reasons for investing.
Consider Diversification: Treat Bitcoin like a high-risk asset. It may offer diversification benefits, but it’s not a guaranteed safe haven.
Stay Informed About Regulations: Follow policy developments. Changes in law can radically alter Bitcoin’s trajectory.
Evaluate Custody and Security Options: Ensure you have a secure storage solution. If you’re unsure, consider professional custodians familiar with digital assets.
Conclusion - Bitcoin’s Uncertain Yet Intriguing Future
Bitcoin began as a response to trust-based financial flaws. It introduced the idea that currency need not be government-issued and that value can move freely across borders without intermediaries. After just 15 years, Bitcoin has grown from a niche experiment to a global topic of debate, speculation, and investment.
Is Bitcoin the “digital gold” of the future, a passing speculative mania, or something in between? The truth lies somewhere amid its rapid evolution, regulatory challenges, and broadening utility. History suggests that no system is permanent, and today’s trust-based frameworks may evolve or crumble. Bitcoin, for all its controversies, represents a new chapter in financial innovation—one that asks each of us to question old assumptions and consider new ways of storing and transferring wealth.
In a world of uncertainty and change, Bitcoin’s ultimate significance remains an open question. Yet its very existence ensures that the conversation about money—how it’s issued, valued, and controlled—will never be the same again.
However, bitcoin's lack of intrinsic value makes it highly vulnerable to external shocks. Its future depends entirely on someone else paying more, and if the crowd (the herd) loses confidence, the trend could quickly spiral in the opposite direction.
SCC views:
Long term - Underweight > Short term - Sell
Take Your Investments to the Next Level: We provide in-depth, research-driven insights on the leading companies shaping tomorrow’s wealth landscape—spot future leaders and grow your portfolio with us.
Risk Warning: The value of investments and the income derived from them may fall as well as rise. You may not get back what you invest. This communication is for general information only and is not intended as individual advice. Seek professional guidance before taking action. Tax treatments are based on current law and may change. Opinions expressed are those of the authors and may not reflect future events.
Check out our website: www.silvercrosscapital.com